According to Precedence Research, the quantum computing (QC) industry is a rapidly evolving and expanding field that is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.9% between now and 2030. That being said, however, according to McKinsey’s estimation, operational quantum computers are only expected to reach about 5,000 by then but, when they do, they will change the world as we currently know it.
What Is Quantum Computing?
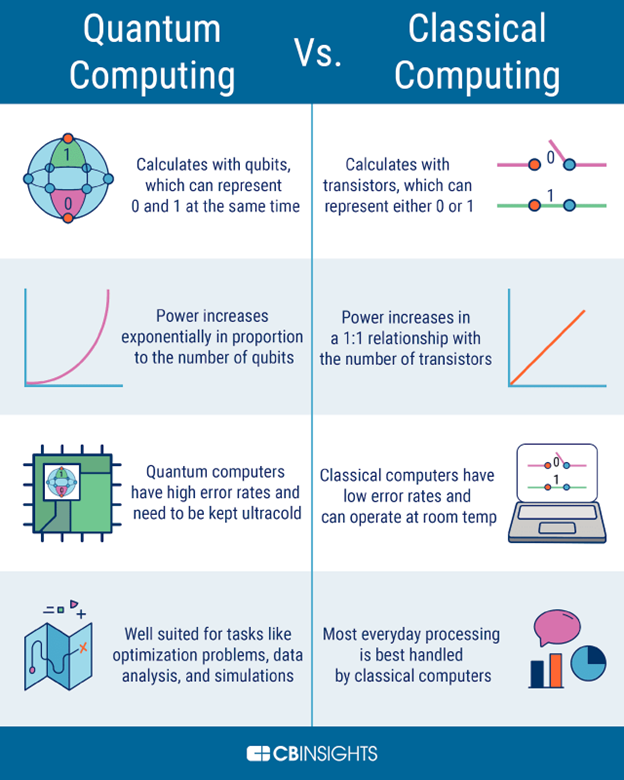
The better the computing power, and the more data, the better a semiconductor will perform and, as such, the race is on for companies to radically upgrade the computing power of their models and that’s where QC comes in. Computers currently operate on a binary system that is equipped with chips that use bits to perform computations but these bits can only show a value of zero or one and, as a result, it takes a lot of zeros and ones arranged in specific orders for a computer to do anything. (Check out this video on Quantum Computing: 4 Things You Need to Know.)
QCs, however, operate with subatomic particles that use quantum bits (qubits) to allow the particles to exist simultaneously in more than one state which increases processing speeds dramatically – and quicker processing speeds mean that computers can tackle more complex problems, which will improve predictive analytics, pattern recognition and complex optimization tasks.
As explained above, present day “classical” computers operate on a binary system that is equipped with chips that use bits to perform computations. These bits are limited, though, and can only show a value of zero or one, so it takes a lot of zeros and ones arranged in specific orders for a computer to do anything.
The research, development and leveraging of “quantum” computers is underway, however, operate with subatomic particles that use quantum bits (qubits) to allow the particles to exist simultaneously in more than one state dramatically increasing processing speeds dramatically – and quicker processing speeds mean that computers can tackle more complex problems, improving predictive analytics, pattern recognition and complex optimization tasks.
Building a QC is extremely expensive, complex and massive, and needs to be kept in stable laboratory conditions, and cooled to nearly absolute zero (-459 degrees Fahrenheit) so, while there are close to 200 companies whose primary focus is on QC Software, according to The Quantum Insider, just over 20 companies worldwide are working on QC Processors and Chips.
Only 4 companies are researching and developing quantum computers exclusive of anything else and they are as follows:
- Rigetti Computing (RGTI):
- specializes in superconducting qubit technology and has developed a suite of software tools and algorithms for programming and simulating quantum computations
- D-Wave Computing (QBTS):
- focuses on quantum annealing technology
- Quantum Computing Inc. (QUBT):
- developing photonic qubits that offer a number of key advantages over trapped ions or superconducting qubits
- IonQ (IONQ):
- planning to build a network of quantum computers accessible via the cloud using trapped-ion technology in its processing units which relies on suspending ions in space using electromagnetic fields, and transmitting information through the movement of those ions in a “shared trap”.
Please note: For
- a specific stock price performance (currently, yesterday, over the past 5 days, 1 month, 6 months and 1 year) go HERE, type in the Stock Symbol, and Click on Time Period
- a specific stock’s performance statistics and financials go HERE, type in Stock Symbol, and Click on Statistics and Financials
- the reasons behind the price change in a specific stock go HERE and ask “Why did x stock change price so much this week?”
- the latest articles and analyses go HERE, type in Stock Symbol, and Scroll down to Recent News